Crypto Terms Explained
Stop wondering what those complex NFT, Web3, and crypto terms mean. We’re here to break down crypto lingo in simple terms.
NFT, WEB3 & CRYPTO TERMS DICTIONARY
Learn the Lingo – Learn Crypto Terms
Many complicated crypto terms are floating around out there. But we’re here to break it down. So, next time you hear NFT, Web3, or crypto lingo, you’ll know exactly what’s going on.
A
Crypto terms beginning with “A”.
ALPHA
Technically speaking, alpha is an investment’s ability to outperform the market. However, you may hear crypto influencers and other Web3 and NFT investors say something like – “I have some alpha for you”. What they mean by this is that they have some good intel. That is, they have exclusive information that others in the market are not aware of yet.
Good Web3, NFT, and crypto influencers spend endless hours researching and examining projects. This can help them find hidden gems and uncover valuable information. However, not all influencers are trustworthy. Before listening to a crypto influencer who says that he or she has reliable alpha, do your own research. At Daily Crypto Guide we never recommend investing in crypto, NFT, or other Web3 projects based on the word of anyone. Always do your own research – and never invest more than you are willing to lose.
ALTCOIN
Any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. For example, Ethereum, Cardano, XRP, Dogecoin, etc.
APE IN
The term “ape in” is a common saying used by crypto investors. Ape in means to throw your money into a coin. Often cryptocurrency holders ape into projects because they are worried they will miss out on massive gains if they don’t act quickly.
APY
APY stands for Annual Percentage Yield. This term is often used in finance. It refers to the annual interest that you will earn on your money. In the crypto world, APY often refers to the amount of interest you will earn each year when staking your crypto.
ATH
ATH stands for All-Time High. The term all-time high refers to the highest price a given crypto coin or token has ever reached.
For example, Bitcoin’s current ATH is $68,789.63. Bitcoin reached this all-time high on November 10, 2021.
B
Discover all the crypto lingo beginning with “B”.
BAG
The term “bag” refers to a crypto investor’s holdings of a particular coin or token. For example, if a crypto holder says – “I have a bag of XRP” – this means that they hold XRP tokens.
Although there’s no specific number of coins or tokens in a “bag”, this crypto term typically describes a significant quantity. So, if someone says they hold a bag of something, this usually means they have a higher-than-average quantity of that particular asset.
BAG HOLDER
A bag holder is a crypto investor who HODLs their investment too long. In some cases, bag holders can get stuck with worthless assets. This commonly occurs when the investor buys the asset at its peak price and misses their opportunity to sell before other holders sell and the price goes down.
BEAR
A bear is a crypto investor who expects that the price of cryptocurrency will fall (in the short term, at least).
BEAR MARKET
A bear market is a period in which cryptocurrencies are stagnant or decreasing in value. Many crypto investors recognize that it’s during a bear market that millionaires are made. This is because, during a bear market, crypto coins and tokens can often be purchased for a fraction of their price. Hence, by buying crypto at low bear market prices, you can make more money when the bull market comes around.
BEAR TRAP
The term bear trap is often used to describe a situation in which crypto investors expect the price of a cryptocurrency to fall but it increases instead. As a result, any “bears” that chose to sell or short the asset (i.e. bet that the price would fall) will be blindsided by higher prices. Hence, a bear trap is a trap for bearish investors.
BLOCK
A block is a set of data within a blockchain. Blocks permanently store transaction data.
Each block can hold a specific amount of info. For example, each Bitcoin block can hold 1 MB of data. Although this doesn’t seem like a lot, it is enough to store more than 2000 transactions! Once this limit is reached, the data is validated, and the block is closed. The closed block is then “chained” to the block completed before it, and a new block is formed (hence the name block-chain).
BOLLINGER BANDS
What are Bollinger Bands, and what do they show? Bollinger Bands are a technical indicator used by many crypto traders to show whether the price of a cryptocurrency is relatively high or low. Bollinger Bands are one of crypto’s most popular technical indicators because they work well with volatile price movements.
Bollinger Bands consist of three bands:
- Middle band – the middle Bollinger Band is the Simple Moving Average (SMA).
- Upper band – the upper band is the SMA plus two standard deviations.
- Lower band – the lower Bollinger Band is the SMA minus two standard deviations.
When the market is volatile, the distance between the bands increases. This is known as the expansion phase.
When the crypto market is less volatile, the distance narrows. This is known as the contraction phase. The contraction phase often signals a good buying opportunity. Buying during the contractions phase can help you capitalize on upward price movement when the crypto returns to an expansion phase.
Below is an example of Bollinger Bands on the Bitcoin chart.

Crypto traders use this information to determine good entry and exit points. For example:
- When the price hovers near the lower band (or breaks through the lower band), this is often a good time to buy.
- When the price hovers near the upper band (or breaks through the upper band), this is often a good time to sell.
- If the price hovers around the SMA, this is referred to as “no man’s land” – in other words, it isn’t a good time to buy or sell.
Remember that Bollinger Bands should always be used with other indicators to determine when to buy and sell crypto. In fact, no technical indicator can reliably show price trends on its own.
BULL
A bull is a crypto investor who believes the price of cryptocurrency is on an uptrend and will continue to increase.
BULL MARKET
A bull market is when cryptocurrencies are increasing in value. In fact, many cryptocurrencies reach new all-time highs during bull markets. Therefore, many crypto investors make great financial gains during this part of the crypto cycle.
BULL TRAP
A bull trap is a scenario in which crypto investors expect the price of a cryptocurrency to increase, but it falls instead. This situation is the exact opposite of a bear trap. In this case, any bullish investors who bought an asset expecting its price to increase will be blindsided by lower prices. Hence, a bull trap is a trap for bullish investors.
BURN
To burn cryptocurrency means to remove a certain number of coins from circulation. For example, when the Stellar Lumens team burned 55 billion XLM tokens in 2019, they permanently removed these coins from the market.
Coins are burned by transferring them to a ‘burn wallet’ or ‘burn address’. Once sent to this address, the coins are lost forever, as the private key for the wallet is unknown.
Developers often burn tokens as a way to increase price. How does this work? Well, burning coins decreases the circulating supply. As a result, scarcity and demand increase, driving the price per coin up.
Some well-known cryptocurrencies that burn tokens include Ethereum (ETH), Binance Coin (BNB), and Bitcoin Cash (BCH).
BUY THE DIP
What does it mean to buy the dip in crypto? When you hear a crypto influencer or analyst tell you to “buy the dip”, what they mean is take the opportunity to buy a crypto coin or token while the price is down. In other words, the phrase “buy the dip” describes the opportunity to invest in a crypto project that has experienced a short or long-term price reduction.
Ok, that makes sense. But does buying the dip work with crypto? The answer is – yes, it can. Buying the dip can work well for crypto investors who are patient and consistently buy the dip. It allows investors to buy strong projects at a discounted price.
That said, dollar-cost averaging has proven to be the most effective strategy for investing in crypto.
C
Crypto lingo that starts with “C”.
CBDC
CBDC stands for Central Bank Digital Currency. A CBDC is a digital form of a country’s fiat currency. Unlike decentralized cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are issued by a centralized authority (i.e. the central bank).
CEX
CEX stands for Centralized Exchange. In contrast to a DEX, a CEX is a privately-owned cryptocurrency exchange that is operated by a central authority (i.e. a business). To facilitate crypto trades, a centralized exchange keeps an order book. This order book matches (quantity and price) buy and sell orders from exchange users. Once a match is found, the CEX executes the order.
Learn more about how a CEX works, and the difference between centralized and decentralized exchanges here – coming soon.
CRYPTO
Crypto is short for cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency is virtual currency that can be used to purchase goods and services or as a store of value. The term cryptocurrency can be broken down into two parts:
1. Crypto – this refers to a process known as cryptography. Cryptography is used to secure crypto transactions.
2. Currency – a medium of exchange. Crypto is used as a medium of exchange and functions like traditional currencies, but with many more benefits.
Learn more about cryptocurrency and how it works here – What is Cryptocurrency?
CRYPTO DERIVATIVES
What are crypto derivatives? Well, if you’ve ever heard of derivatives in the stock market, crypto derivatives work in the same way as traditional derivatives. If you’re still not sure what we’re talking about – no worries, that’s what we’re here for!
A crypto derivative is a contract for the sale/purchase of an underlying asset (i.e. a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin). This contract establishes a predetermined sale/purchase price and time. Prices for derivatives are determined by the price of the underlying asset. Therefore, a derivative does not have any inherent value (because the contract relies on the value of the underlying asset).
Ok – WTH does this all mean?! Here’s an example to help clarify.
Let’s say that on September 1, 2022, Bill buys a contract for Bitcoin at a price of $30,000 per BTC. The contract expires on December 1, 2022. This means that Bill must purchase Bitcoin at this predetermined price when the contract expires. This type of derivative is also known as a futures contract. Essentially, it is a contract for the future sale of an asset – hence, “futures”.
There are also other types of derivatives. Options, for example, are very similar to futures. The biggest difference between futures and options is that with options, the buyer is not obligated to purchase the asset. In other words, they have the “option” to purchase the asset for the pre-determined price or to let the contract expire.
CRYPTO INFLUENCER
A crypto influencer, like any influencer, is someone who has built a strong presence and large following online. They use their platform to share their ideas and knowledge about all things related to cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. For instance, some crypto influencers share their knowledge of TA, their market predictions and current trades, and even ideas about price fluctuations based on moon cycles!
A crypto influencer may be a celebrity, an expert on the topic, or just a regular person who has built a large following.
Some examples of crypto influencers include:
- Vitalik Buterin – @VitalikButerin
- Tom Crown – @TomCrownCrypto
- CryptoWendyO – @CryptoWendyO
- Vivian – @blockchainedbb
- CryptoWeatherMan – @CryptoWeatherMan
- Lady of Crypto – @LadyofCrypto1
- MAREN – @marenaltman
- Pablo Heman – @RealPabloHeman
CRYPTO WINTER
Wondering – what is crypto winter? Crypto winter refers to a prolonged period of low crypto prices (usually months or years). In addition to lower than average prices, crypto winters are characterized by FUD (i.e. low sentiment) in the market. It is typical to hear the media and news outlets claim that “Bitcoin is dead” during a crypto winter.
Crypto winter is the same as a bear market.
Because cryptocurrency is such a new asset class, crypto winters can bring significant price drops. For instance, coins can plummet 99% (or more) from their ATHs.
Even so, many crypto investors welcome crypto winter with open arms, as it gives them time to accumulate quality crypto coins and tokens for a fraction of the price.
That said, investors (especially new crypto investors) should be careful during crypto winter. This is because many crypto projects, especially altcoins, will not recover and could even go to zero.
D
Learn crypto terms that start with “D”.
DAO
DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization. A Decentralized Autonomous Organization is a corporation that is not directed by any individual or central authority. Instead, rules and decision-making processes are predetermined and encoded into the program (known as a smart contract) by developers. These preset rules are completely transparent and initiated automatically by the smart contract (hence, “smart”).
Certain decisions are also made using a democratic voting system. In other words, all the individuals who have invested in the DAO can vote on these decisions. Decisions are implemented automatically based on the outcome of the vote.
The goal of DAOs is to eliminate human error and corruption.
DAPPS
Dapps stands for Decentralized Applications. Decentralized Applications are similar to traditional apps. However, unlike normal apps, dapps run on blockchain technology. This means that no single company (e.g. Apple) has control over the distribution of dapps.
Dapps are open-source. This means that the app’s code is public. As a result, the code can be modified and shared. The information and records held by dapps are also transparent and available to the public.
DCA
DCA stands for Dollar-Cost Averaging. This refers to a popular investing strategy in which investors buy crypto consistently over time. Those who dollar-cost average into an investment make regular purchases, regardless of price. This strategy is often very effective, as it removes the emotional aspect of crypto investing.
It is extremely hard to time the very bottom of a cryptocurrency’s price (i.e. to enter at the perfect moment). Therefore, by purchasing crypto consistently over time, investors can get the best average price.
DCA Example: buying $100 of Bitcoin each week, regardless of price.
Keep in mind, crypto investors can also use the DCA strategy when selling cryptocurrency. This means selling small increments of crypto as the price increases. This helps investors make the most of their investment – without having to perfectly time the top. You may hear this referred to as “dollar-cost averaging out”.
DEAD CAT BOUNCE
A dead cat bounce is a temporary and short-term recovery in crypto prices after a substantial decline. This term is often used in crypto but first originated on Wall Street.
A dead cat bounce is sometimes referred to as a Sucker Rally. It earns this name because many investors believe that this uptrend signifies a reversal in the market (i.e. that prices will continue to go up). As a result, they start to buy but are sorely mistaken when prices continue to fall after the short rally.
What causes a dead cat bounce?
There are several common reasons for a dead cat bounce in crypto. This includes:
- Short positions being cleared
- Investors buying because they believe the bottom of the market is in
- Assets being oversold, etc.
DECENTRALIZED
This common crypto term refers to a project with no central authority. In other words, a decentralized project does not rely on an individual or organization. Instead, control and decision-making are handled by a distributed network (i.e. many different entities share control).
That said, the terms decentralized and distributed should not be confused. While decentralized means that no central authority has control, distributed means that computational processes and data storage occur in various locations (see distributed ledger technology).
When comparing decentralized vs distributed blockchains, it is important to note that all blockchains are distributed but not all are decentralized.
DEFI
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance. Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, allows individuals to complete financial transactions without a centralized organization like a bank or government. For example, people can borrow, lend and trade crypto without a centralized institution using DeFi.
The goal of DeFi is to eliminate the control that banks and other large institutions have over money and financial services.
DEX
DEX stands for Decentralized Exchange. A DEX is a crypto exchange that is not controlled by any central organization. Rather, it is a peer-to-peer exchange, meaning that crypto traders can trade coins and tokens amongst each other without the need for centralized oversight. To complete these trades, a DEX uses automated algorithms.
For example, Coinbase is a centralized exchange. This means that a large business oversees all operations and crypto trades – and makes money from it. On the other hand, PancakeSwap is a decentralized exchange. Therefore, no one organization or person has control over it and no business makes money from it. Instead, crypto traders can simply exchange tokens with one another.
There are several other important differences between centralized and decentralized exchanges, including privacy and ownership distinctions. Check them out here – coming soon.
DIAMOND HANDS
The crypto term “Diamond Hands” refers to someone who holds their crypto no matter what is happening in the market. Regardless of volatility, a person with diamond hands will not sell their crypto.
DLT
DLT stands for distributed ledger technology. Put simply, DTL is a way of recording, storing, and sharing information.
A distributed ledger is similar to a database. Like a traditional database, a distributed ledger is used to store data (e.g. transactions). However, unlike a typical database (which stores its data in one place), DLT uses multiple computers (often referred to as nodes) to store data in various locations. In other words, records are distributed across many different computers.
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger.
DOXXED
You may have come across the term “doxxed” in your crypto research. Most often, this refers to a cryptocurrency project team. If a crypto or NFT team is doxxed this means that they have shared their personal information with the public. For example, a fully doxxed team will publish their real names, background, work history, pictures, etc. This helps to build trust within the community.
When researching a new crypto project, always look for a team that is fully doxxed. Why? Well, teams that share their personal details publicly are much less likely to be involved in rug pulls*.
*Note that we said “less likely”. Even cryptocurrencies with fully doxxed teams can fail.
DYOR
DYOR stands for Do Your Own Research. This is a best practice for investors and something that many crypto influencers and educators emphasize – including your friends at Daily Crypto Guide!
It’s extremely important that you always do your own research before investing in crypto (or any investment for that matter), regardless of what others recommend. You will be putting your hard-earned money at risk. Therefore, it’s essential that you know exactly what you are investing in.
That said – what does it actually mean to “do your own research”? Well, in the case of cryptocurrency, this means looking into the project’s team, understanding its utility and use cases, and keeping up with the latest news and achievements of the project.
E
Crypto terms starting with “E”.
Stay tuned for “E” crypto terms.
F
Discover crypto lingo beginning with “F”.
FDV
FDV stands for Fully Diluted Valuation. A coin’s FDV is its total market cap if all tokens were in circulation. You can find the FDV of any coin by multiplying its current price by the total supply.
For example, if the cost of Bitcoin on a given day is $50,000, its fully diluted valuation is 50,000 x 19,000,000 (total maximum supply) or 950,000,000,000 (i.e. 950 billion).
FIAT
Fiat is government-issued money. In other words, fiat is the legal tender of a country. Examples of fiat money include the U.S. dollar (USD), Canadian Dollar (CAD), European Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), etc.
FUD
FUD stands for Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt. Periods of FUD often occur when negative news and general fear rule the crypto market. Negative events in the crypto space commonly provoke FUD. However, in many cases, these events are exaggerated or even completely fabricated.
FUD often prevents people from participating in the NFT, Web3, and crypto markets because they are uncertain of what the future holds.
G
Cryptocurrency lingo beginning with “G”.
Stay tuned for “G” crypto terms.
H
Learn crypto terms that start with “H”.
HARD FORK
What is a hard fork in cryptocurrency? A hard fork is a dramatic upgrade to a blockchain that requires a new version to diverge (or “fork”) from the current version.
A hard fork in cryptocurrency is only required when an upgrade to a blockchain is so drastic that is causes previous blocks to become invalid. As a result, two versions of the blockchain must exist separately – one version using the old set of rules and the new version using a new set of rules.
One of the most well-known examples of a hard fork is Ethereum. In June 2016, Ethereum was hard forked from the original Ethereum Classic blockchain when a smart contract called the DAO was hacked.
Learn more about Ethereum and the DAO hack here – What is Ethereum?
Keep in mind that not all blockchain upgrades result in a hard fork. Less drastic changes can result in a soft fork.
HIGH-CAP
A high-cap (or large-cap) is a cryptocurrency with a market cap of more than $10 billion. Typically, large-cap cryptos are those in the top 10. Examples of high caps include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Although all cryptocurrency carries some risk, high-cap projects are considered to be relatively safe investments.
HODL
HODL stands for Hold On for Dear Life. This common crypto term describes the strategy of buying and holding cryptocurrency (even through the ups and downs of the market). The term was first introduced when someone (explaining that he would HOLD his Bitcoin) misspelled “hold”. Very quickly the term became a meme. Now, hodl is used widely throughout the crypto community, especially during times of extreme volatility.
I
Cryptocurrency terms starting with “I”.
ICO
ICO stands for Initial Coin Offering. An ICO is similar to an IPO (Initial Public Offering). However, ICOs are used to raise funds for new crypto projects.
Investors who take part in an ICO receive tokens before they are listed on any exchange. These tokens may offer utility related to the project or simply allow the investor to get in on the project early.
IDO
IDO stands for Initial DEX Offering. An IDO is similar to crowdfunding – but for crypto projects. When an IDO is used to raise funds for a new cryptocurrency project, the project’s coins or tokens are listed on a decentralized exchange (DEX).
The main difference between an IDO and an ICO is that with an IDO the project’s coins or tokens are listed on an exchange (i.e. a DEX). On the other hand, with an ICO, coins and tokens are sold before they are listed on any exchange.
ISO 20022
ISO 20022 (pronounced “I-S-O twenty-oh-two-two”) is a global, standardized language for financial messaging. Financial institutions will use ISO 20022 to create and send electronic messages that follow the same structure, form and meaning. In other words, ISO 20022 will create a common language for payments worldwide.
This standardized language will allow financial institutions across the world to exchange financial transaction data more effectively and efficiently. As a result, interoperability will increase, allowing financial institutions worldwide to communicate more easily.
J
Crypto terms that start with “J”.
Stay Tuned.
K
Discover lingo starting with “K”.
KYC
KYC stands for Know Your Customer. Crypto exchanges use this process to verify the identity of their users. KYC is also used by many financial institutions. The goal of this process is to help eliminate money laundering and other illegal activities. To complete KYC requirements, you’ll need to provide proof of your identity (i.e. usually with a photograph) and proof of address (e.g. by providing an image of your Driver’s License).
L
Crypto terms that start with “L”.
LIQUIDITY
Wondering – what is liquidity in cryptocurrency? This crypto term refers to how easily you can convert an asset into cash or another asset – without affecting its price. For instance, how easily you can convert a coin or token into another coin or fiat.
What does it mean if an asset has good liquidity (i.e., the asset is liquid)? An asset with good liquidity can be quickly and easily bought or sold. In addition, buying and selling large amounts of a liquid asset will not have much effect on its price.
Cash, for instance, is an extremely liquid asset. In fact, it is the most liquid asset on earth and can be quickly and easily converted into other assets. In crypto, stablecoins are the most liquid assets.
What about assets with poor liquidity (i.e., illiquid assets)? An illiquid asset can’t be bought or sold easily. Also, if an asset is illiquid, it is difficult to exchange it without significantly impacting its price.
For example, exotic cars, rare books, and artifacts are considered relatively illiquid because selling them isn’t always easy.
When it comes to crypto, large-cap cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum don’t have issues with liquidity. However, some altcoins (especially low-cap coins) may lack liquidity.
If you invest heavily in illiquid coins, you may get stuck holding the bag – without the ability to sell at your desired exit price. Thus, it’s generally safer to trade assets with reliable liquidity.
LOW-CAP
Low-cap (or small-cap) refers to a cryptocurrency with a low market capitalization. A low-cap crypto has a market cap of less than $1 billion. Typically, low-cap cryptocurrencies are still in early stages of development. As a result of their low market capitalization, low caps are the most susceptible to wild price swings due to market volatility.
M
Discover crypto lingo starting with “M”.
MAINNET
A mainnet is a fully developed blockchain platform that is ready for public use. In other words, a mainnet is a blockchain project that has been tested and deployed. This is in contrast to a testnet which is still in the development stages.
Like a testnet, developers can update and revise a mainnet whenever they wish.
MARKET CAP
In crypto, the market cap of a coin is the total value of all the coins (of that kind) in circulation at a given time. To find the market cap, simply multiply the price of the coin (current price) by the number of coins in circulation.
Market Cap = Current Coin Price x Number of Coins in Circulation
The market cap of a project is important for a number of reasons. Most importantly, the market cap helps crypto inventors compare coins and gauge a coin’s potential for growth. The market cap of a cryptocurrency can also help investors determine how risky it is. For example, micro-cap coins are much riskier than established high-cap (large-cap) cryptos like Ethereum.
That said, investing in crypto is risky, no matter how large a coin’s market cap is. Therefore, you should never invest more than you are willing to lose.
MICRO-CAP
A micro-cap is a cryptocurrency with a very small market cap. Typically, micro-cap coins have a market cap under $50 million.
Compared to high-cap vs mid-cap vs low-cap, micro-cap altcoins are the riskiest. Why? Well, micro-cap projects have a higher risk of being rug pulls because they are so new and not yet established. Due to the fact that the market cap is so low, whales can easily manipulate the price. That said, micro-cap coins also have the potential for the biggest gains in the crypto space.
If you do decide to invest in risky micro-cap coins, be sure to do your research. Look for projects with strong partnerships and teams that are fully doxxed. And, of course, never invest more than you are willing to lose.
MID-CAP
A mid-cap crypto is a cryptocurrency with a market cap between $1 billion and $10 billion. Mid-cap cryptos are not as risky as low-caps. However, they are riskier than high-cap cryptocurrencies. That said, mid-caps often have more potential for growth than high caps. As a result, many people invest in mid-cap cryptocurrencies in an attempt to maximize their return on investment.
MOON BAG
A moon bag is a bag of crypto that an investor holds that consists of profit only. In other words, the crypto holder bought the coin or token at a low price and sold it high, allowing them to take out their initial investment plus profit. As a result, they still hold some of the coins or tokens but none of their own money is at risk. If the crypto continues to increase in value, they’ll earn more profit. And, if it crashes, they have nothing to worry about. Essentially, this is like playing with “house money”
The “moon bag strategy” was made popular by top crypto influencers like CryptoWendyO.
N
Learn crypto terms that begin with “N”.
NFA
NFA stands for Not Financial Advice. Crypto influencers and educators (as well other financial educators) often use this term to remind viewers that they are not financial advisors. Therefore, the knowledge they share is not financial advice but, instead, for informational purposes only.
Only certified financial advisors can provide sound financial advice – and most people online are not financial consultants. Therefore, it’s very important to DYOR before investing in any crypto project.
NFT
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token. A non-fungible token is a unique token that is unlike anything else.
To make this idea clearer, consider a single dollar vs a baseball trading card. You could swap your dollar with your friend’s dollar and there would be no difference. The two dollars are (essentially) the same. However, if you were to swap an extremely rare baseball card with your friend’s not-so-rare card, there could be an issue. These two cards are completely different and it’s unlikely you would want your friend’s card in exchange for your more valuable collectible. These basecall cards are non-fungible.
The idea behind NFTs is similar to baseball trading cards. An NFT can be traded or sold and no two are alike.
Some popular NFTs you may have heard about include Bored Ape Yacht Club, World of Women, and Azuki. These NFTs can sell for hundreds of thousands of dollars.
NODE
In blockchain and crypto, a node is a computer that participates in a blockchain network. Nodes run blockchain software and have two main purposes:
- Validate and record new data and transactions
- Store a copy of the entire blockchain
O
Crypto lingo starting with “O”.
OPEN SOURCE
The term “open source” originated in the computing science sector. Open source refers to software with code that is accessible to anyone. That is, anyone can view, modify and share the code. Open source software is developed by a community rather than an individual or company.
Using open source code, crypto and blockchain projects can be developed in a collaborative and decentralized way. In addition to supporting decentralization, open source code also has several other benefits, including being more:
- Cost-effective
- Flexible
- Likely to stand the test of time
ORACLE
Are you wondering – what is an oracle in crypto? Although it might sound complicated, this crypto term is not tricky to understand. Essentially, an oracle is a bridge that connects blockchains and smart contracts to the outside world. In other words, an oracle feeds data from the outside world into a smart contract and vice versa.
Why are oracles needed in crypto? Blockchains and smart contracts cannot access data outside of their network. However, outside information is often required to execute smart contracts. Therefore, oracles are needed to bridge the gap between on-chain and off-chain data.
Without oracles, smart contracts would have limited use cases, as they would only have access to specific data. But, with the help of oracles, blockchain technology and smart contracts can be used in many more industries and use cases.
OTC
OTC stands for Over-The-Counter. OTC trading, or over-the-counter trading, allows crypto investors and traders to buy and sell crypto privately. In other words, rather than using a typical exchange, OTC trading allows participants to exchange coins and tokens directly. That is, the two parties trade directly with one another, rather than using a middle-man (i.e. a broker or crypto exchange).
P
Learn crypto terms that begin with “P”.
PAPER HANDS
Crypto enthusiasts often use the term “paper hands” to describe someone who sells their crypto at the first sign of trouble in the market. You can think of someone with paper hands like a poker player who folds too easily.
People with paper hands are not comfortable with volatility. Therefore, they sell their crypto whenever they see the market going down. In most cases, investors with paper hands sell too early, resulting in unnecessary losses.
Q
Crypto lingo starting with “Q”.
STAY TUNED.
R
Crypto terms that begin with “R”.
RSI
RSI stands for Relative Strength Index. It is a market trend indicator that stock and crypto traders use when performing technical analysis. RSI is a very common indicator used by crypto traders.
More specifically, the Relative Strength Index shows whether a cryptocurrency is overbought or oversold. To provide this insight, the RSI formula considers a cryptocurrency’s average price gain vs average price loss over a certain period. Using this data, traders can see whether the asset is overbought (i.e. RSI is equal to or greater than 70%) or oversold (i.e. RSI is equal to or less than 30%).
The rule of thumb when using the RSI indicator is to buy when a cryptocurrency is oversold and to sell when a crypto is overbought. This is because an oversold asset will likely experience an upcoming uptrend, and an overbought asset will most likely experience a downtrend soon.
Below is an example of the RSI indicator on the Bitcoin chart. When the purple line (RSI) is above the horizontal dashed line (i.e. above 70), Bitcoin is overbought. This is often a good time to sell. When it is below the dashed line (i.e. 30), it means that Bitcoin is oversold. This is often a good time to buy.
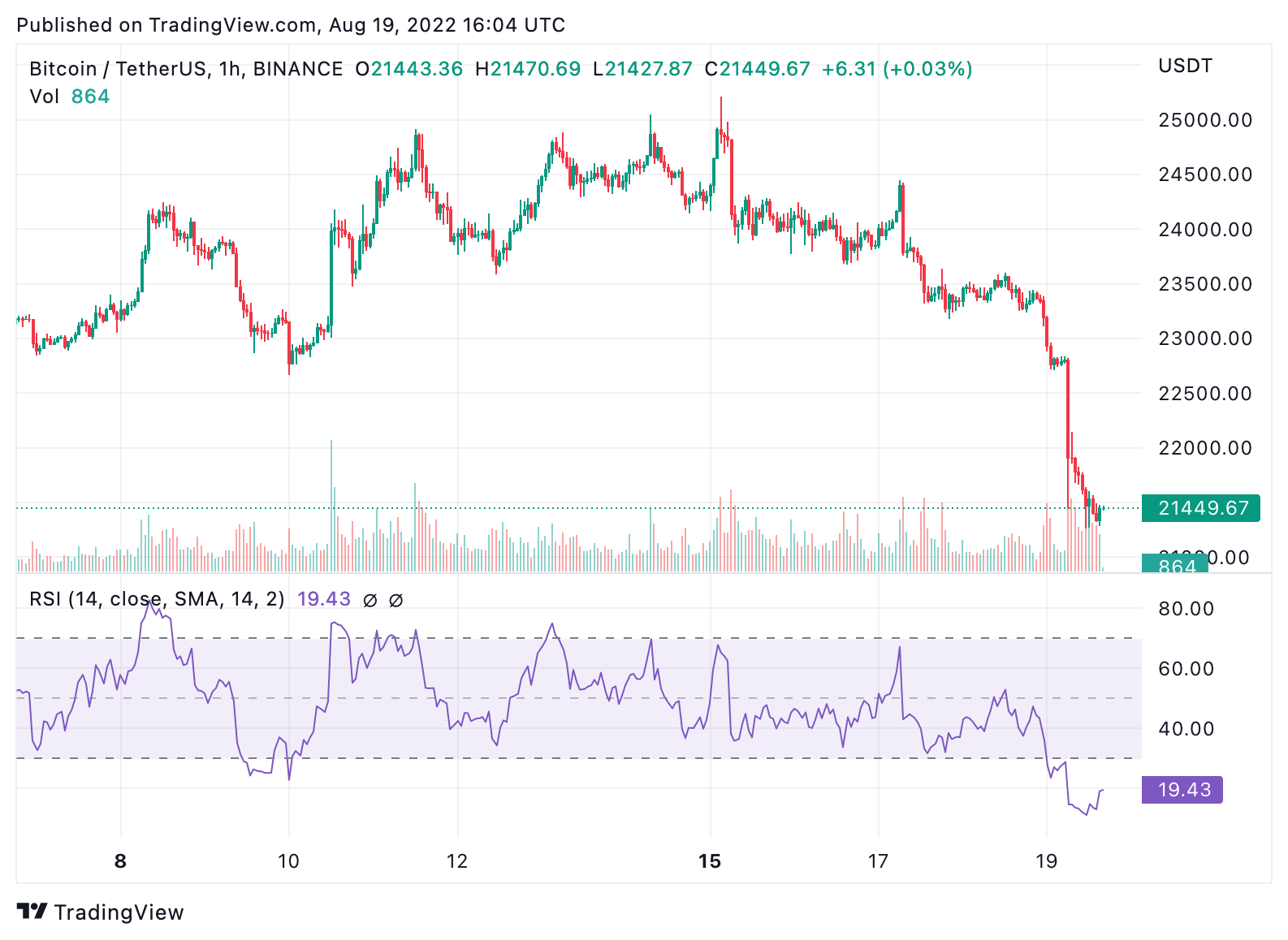
The best crypto trading platforms will allow you to add an RSI line graph below your market charts at the touch of a button. Therefore, using RSI to predict market trends is easy!
Keep in mind that RSI should always be used with other technical indicators to predict trends and prices better.
RUG PULL
A rug pull is a type of scam in the crypto industry. A rug pull occurs when a project team heavily promotes their coin, token, or NFT, then abandons the project and runs off with investors’ money.
Typically, in a rug pull, the project developers hold a significant number of coins or tokens. They promote or “shill” the project online and once the price goes up they quickly sell. This often causes the price to fall to zero, meaning investors lose everything.
S
Crypto lingo beginning with “S”.
SEED PHRASE
What is a seed phrase? This crypto term refers to the secret code that allows you to recover your crypto wallet. A seed phrase is composed of 12 to 24 simple words. When you set up your wallet, these words are randomly generated (from a list of 2,048 words).
Here’s an example of what your seed phrase might look like:
abandon aspect bottom capital chest dentist dwarf hazard kick lottery maid novel
You must keep your seed phrase safe and private. This is because you’ll lose access to your crypto wallet if you lose your seed phrase. And, if someone else gets a hold of your seed phrase, they can hack in and steal your crypto!
A seed phrase may also be referred to as:
- Recovery phrase
- Backup phrase
Please note: a seed phrase is not the same as a private key – although both must be kept safe and secure to avoid being hacked.
SHILL
To shill a crypto project means to promote a coin or token for personal financial gain heavily. This is also referred to as “pumping”.
Project teams often pay crypto influencers to shill coins. They do this to attract investors and drastically increase the coin’s price.
It is common for projects that are shilled/pumped to be rug pulls. Therefore, it is essential that you do your own research. Never invest in a crypto project just because someone told you it was going to the moon.
SHO
SHO stands for strong holder offering. Like an ICO or IDO, a SHO is used to raise funds for a new crypto project. However, unlike ICOs and IDOs, SHOs are limited to particular investors. In other words, to participate in a SHO, an investor must meet certain criteria. These investment criteria are set by the crypto project. In many cases, eligibility is determined by a potential investor’s current crypto holdings or recent on-chain activity (e.g. $5,000 in crypto transactions in the previous month).
SHRIMP
In crypto, a shrimp is an investor that holds a very small amount of coins/tokens. The exact amount of crypto a shrimp holds varies depending on the cryptocurrency.
For example, a Bitcoin shrimp is someone who holds less than 1 Bitcoin.
Want to know where you fit in the Bitcoin food chain? Here are the categories investors fall into:
- Less than 1 Bitcoin – SHRIMP
- 1 to 10 – CRAB
- 10 to 50 – OCTOPUS
- 50 to 100 – FISH
- 100 to 500 – DOLPHIN
- 500 to 1,000 – SHARK
- 1,000 to 5,000 – WHALE
- 5,000+ Bitcoin – HUMPBACK WHALE
SLIPPAGE
What is slippage in crypto? You might have seen the term “slippage” when doing your crypto research or placing an order on a decentralized exchange like PancakeSwap. You probably thought to yourself – WTH is slippage? No need to worry, the concept of slippage is a lot simpler than it might seem.
Slippage is simply the difference between the price you expect to pay for your order and the price you actually pay. Cryptocurrency is very volatile. Therefore, the price of an asset can change quickly. When you set a slippage, you are verifying the percentage in price difference that you are ok paying (if the price changes before your order is filled).
There are two types of slippage:
- Positive slippage – traders experience positive slippage when the actual executed price is lower than the expected price for a buy order. This type of slippage is “positive” because the trader gets a better rate than they anticipated.
- Negative slippage – this occurs when the executed price is higher than the expected price for a buy order. In this case, the slippage is “negative” because the trader must pay more for the asset than anticipated.
Keep in mind that these two types of slippage are the exact opposite for sell orders. That is, if the executed sell price is lower than the expected sell price, this is negative slippage. If the executed sell price is higher than the expected sell price, this is positive slippage.
SMART CONTRACT
What is a smart contract (simple explanation)? A smart contract is a digital contract that is stored as a software program on a blockchain. When the predetermined contract conditions are met, the program runs (i.e. the contract executes).
Smart contracts have many advantages, including the ability to execute automatically without the need for a middleman. That said, because a smart contract runs automatically, it cannot be undone. Once you agree to a smart contract, there is no backing out.
Looking for an example? Here’s a Smart Contract Example to help paint a clear picture of how smart contracts work.
SOFT FORK
A soft fork is a blockchain software upgrade that is backward compatible. This means that the upgraded blockchain code will still recognize previous blocks as valid.
This is in contrast to a hard fork. In the case of a hard fork, the new and old versions of the blockchain are incompatible.
STABLECOIN
What is a stablecoin? A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency that, unlike most crypto coins and tokens, is designed to have a relatively stable price. Stablecoins developers attempt to stabilize the price by pegging the coin to an external commodity or fiat currency. The price of a stablecoin can also be stabilized using an algorithm to automatically adjust the coin’s supply.
Examples of stablecoins include:
- USDC (USD Coin) – this stablecoin is pegged to the U.S. dollar
- PAXG (PAX Gold) – this stablecoin is backed by gold
The point of a stablecoin is to minimize volatility. The goal is to create a more stable coin that can be used as an actual digital currency.
STORYTELLING NFT
A storytelling NFT is an NFT that is created based on a story. The aspect of storytelling was previously absent from the NFT space. But, with the introduction of storytelling NFTs, fans can now get involved with the stories they love. Better yet, storytelling NFTs allow community members to contribute to an NFT project by voting on and helping write components of the story!
SWIFT
You may come across the term “SWIFT” in crypto, particularly in discussions about ISO 20022 coins. That’s because SWIFT is ISO 20022’s predecessor.
Ok, but what is SWIFT? Well, SWIFT is an international messaging format for financial transactions. In other words, banks and financial institutions worldwide use the SWIFT language and standardized codes to effectively communicate financial data.
By using this messaging system, financial institutions can communicate quickly, easily, and automatically, regardless of the language spoken by its users.
T
Cryptocurrency lingo that starts with “T”.
TA
TA stands for technical analysis. Technical analysis uses price patterns and technical indicators to predict crypto price fluctuations.
Cryptocurrency investors often use TA to predict prices, including entry and exit points for trades.
Some of the most common technical indicators in crypto include:
- RSI (Relative Strength Index)
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence/Divergence)
- MA (Moving Averages)
- Bollinger Bands
TESTNET
A testnet is a blockchain platform that is still in the development and testing stages. In other words, a testnet is a prototype that isn’t ready for public use.
Developers use testnets to test and troubleshoot projects before releasing them to the public. Once testing, troubleshooting, and development are complete, the project is released via a mainnet launch.
TO THE MOON
“To the moon” is a phrase that is often used by crypto investors and enthusiasts. It refers to the idea that a certain cryptocurrency will rise significantly in price.
For example, you may hear someone say “Dogecoin is going to the moon!”. This means that the individual believes that the price of Dogecoin will skyrocket in the near future.
TOUCH GRASS
You may have heard or seen a crypto influencer tell their followers to “touch grass.” And, you’re probably wondering – What the? Don’t worry; we’re here to explain.
The slang term “touch grass” is commonly used in the crypto community to remind people to stop staring at their screens and to go outside. While touch grass can be used as an insult, crypto educators often use the term to remind people that it is essential to reconnect with the real world – especially the outdoors. Unfortunately, many crypto investors become so enchanted with charts and monitoring their portfolios that they forget there is a whole world outside to enjoy!
So, like other crypto educators, we’re here to tell you not to forget to “touch grass” today!
U
“U” crypto terms explained.
STAY TUNED.
V
Cryptocurrency terms that start with “V”.
VESTING
What is vesting in crypto? This crypto term refers to the time an investor must wait until they gain complete control over an asset they have purchased. For example, tokens sold during an ICO are vested. Crypto tokens cannot be sold, exchanged or traded during this time. Once the vesting period is over, investors gain full control over the assets. This vesting period is also known as a token lockup period.
The purpose of a vesting period in crypto is to help new projects avoid liquidity issues while they are still building a solid foundation.
W
Crypto terms that start with “W” explained.
WAGMI
WAGMI is an acronym for We’re All Gonna Make It. This crypto term is used to boost hope and inspiration within the crypto and NFT communities. The term WAGMI also shows camaraderie between members of the community. In other words, it’s a way to say, “no matter what, we are all in this together.”
WHALE
A crypto whale is an investor who holds a significant amount of cryptocurrency. Although the amount of crypto a whale holds depends on the coin or token, it is common for whales to hold 10% or more of a particular cryptocurrency.
When it comes to Bitcoin, whales are investors who hold 1,000+ BTC.
Crypto whales often hold enough cryptocurrency to manipulate the market. In other words, because they hold so much of the circulating supply of a coin or token, their actions can cause the price to drastically rise or fall. Therefore, many crypto traders watch whales closely for hints at what might happen next in the market.
